In the ninth post in our series looking at the history of Chelmsford High Street, Ashleigh Hudson looks at no. 26 High Street through the centuries. Find out more about the project here.
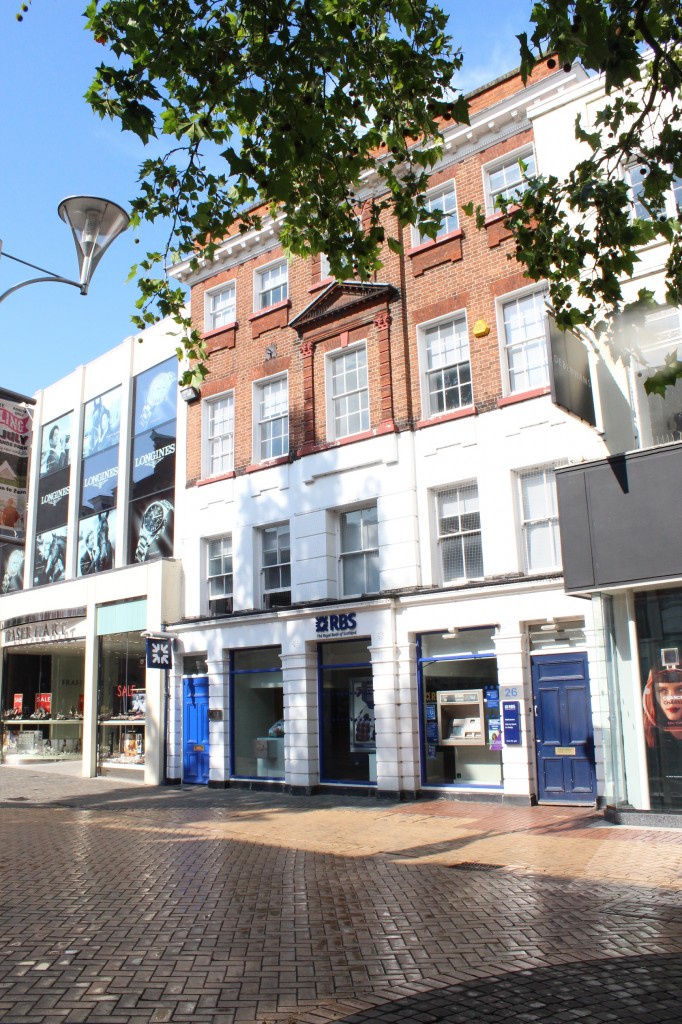
Over the centuries, the lives of a whole cast of characters have played out at no. 26 Chelmsford High Street. Its origins are as a private residence, but it was used during the 19th century as grand lodgings for travelling judges visiting the town. Later it accommodated the Essex Weekly News offices, and today is occupied by the Royal Bank of Scotland.
In the early 18th century the property was owned by the Goodwin family of goldsmiths. They sold it in 1718 to Sherman Wall, an apothecary, who later passed it to his son, also apothecary named Sherman. In about 1738 Sherman’s daughter Amey married Benjamin Pugh, who was himself a child of an apothecary. Benjamin was a surgeon, and a pioneer in the fields of midwifery and smallpox inoculation. As part of their marriage settlement it was agreed that Amy would inherit the site of 26 High Street upon her father’s death. The building on the property must have been substantial, as it is referred to as the ‘mansion house’.

The marriage settlement of Benjamin Pugh and Amy Evans (nee Wall) in which 26 High Street is referred to as the ‘mansion house’, 1738 (D/DU 755/45)
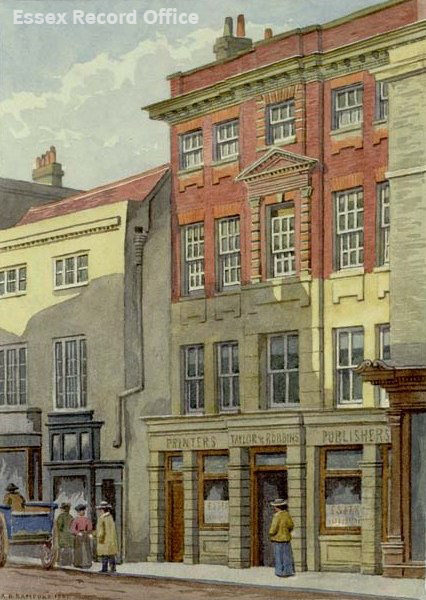
Sherman Wall died in 1744, and by 1755 Benjamin Pugh established full control of the property and had commissioned the demolition of the existing buildings to make way for the handsome red brick four storey town house we see today. Benjamin owned the property until 1772 when he sold it to John Lucy.
For several decades in the 19th century the house was used to accommodate judges who were visiting Chelmsford to preside at the Assizes – periodic courts which heard the most serious criminal and civil cases. The engraving below, by J. Ryland, depicts the grandeur of the Assize procession through the High Street.
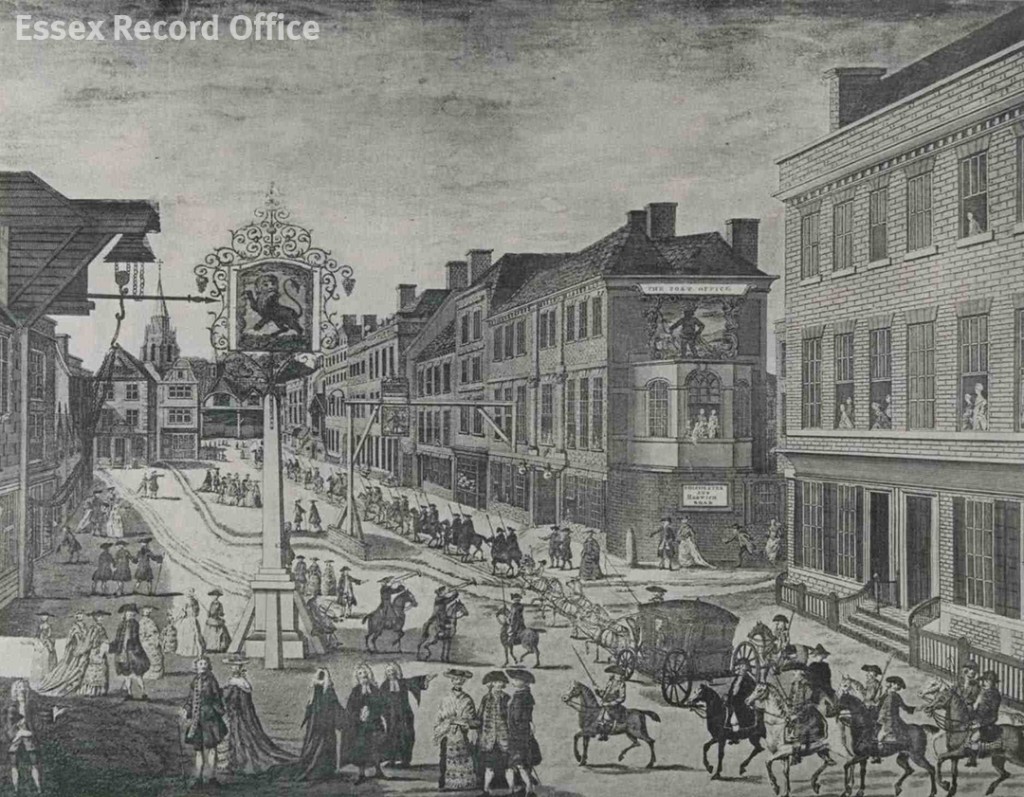

Engraving by J. Ryland depicting the judges’ procession through the High Street prior to the opening of the Assizes. (I/Mb 74/1/109).
These lodgings must have been rather more luxurious than the judges had endured in the past. In 1806, the High Sheriff of Essex, James Urmston, wrote to the chairman of the Quarter Sessions (the county authority which preceded the County Council) highlighting the inadequacy of existing lodgings for the visiting judges. Accommodation had been provided by the Ipswich Arms (site of 73 High Street) which, according to Urmston, was in such a dire state the building faced demolition. Certainly, Urmston thought, the accommodation was not befitting ‘men distinguished by their rank and talents and venerable years of learning’.
The judges requested that their new lodgings should contain two dining or sitting rooms for the judges themselves, a sitting room for attendants, an office for the judges’ officers and clerks, a servants’ hall and large kitchen as well as eleven separate bedrooms.
After spending a few years in temporary lodgings in various private residences, a solution to the judges’ woes was found in the shape of the mansion house. The property had been purchased in 1811 by James Potter, a draper who had intended to use the house as his main residence. Shortly after purchasing it, however, Potter agreed to its use as judges’ lodgings. The judges must have been comfortable there as the arrangement continued until the house was sold in 1849.

Extract from the Sales Catalogue of 1849. The property contains a handsome bold staircase which led to a large suite of rooms on the first floor. The document also mentions that the apartments were recently occupied by the Judges of the Assize. (D/DU 755/45).
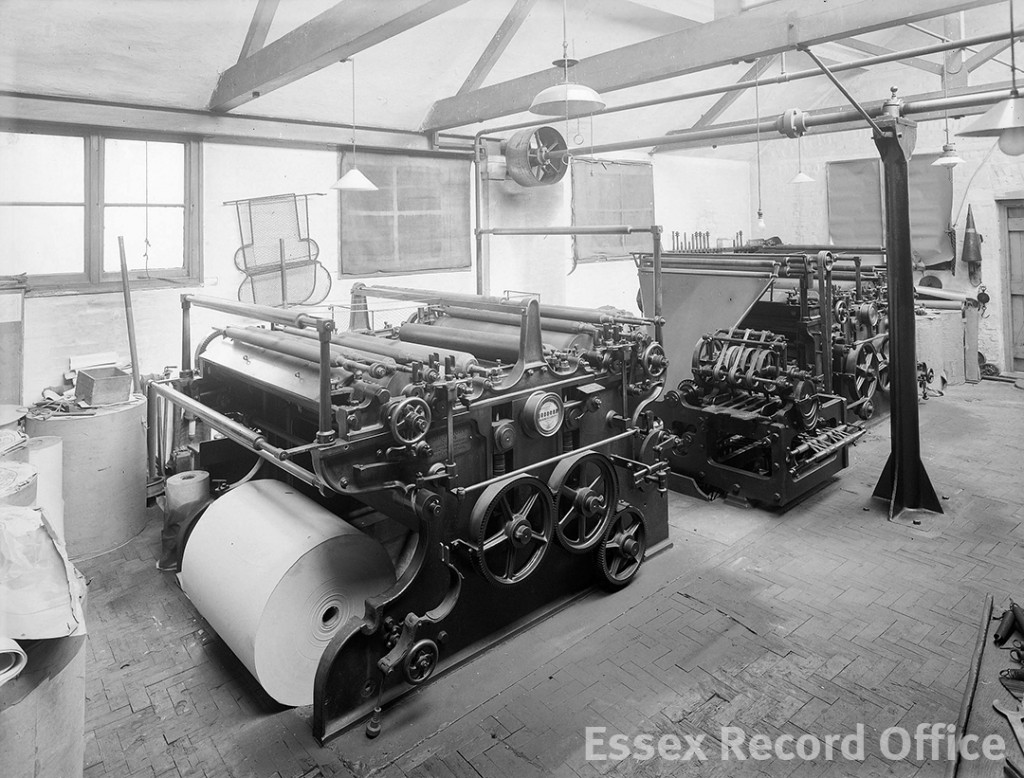
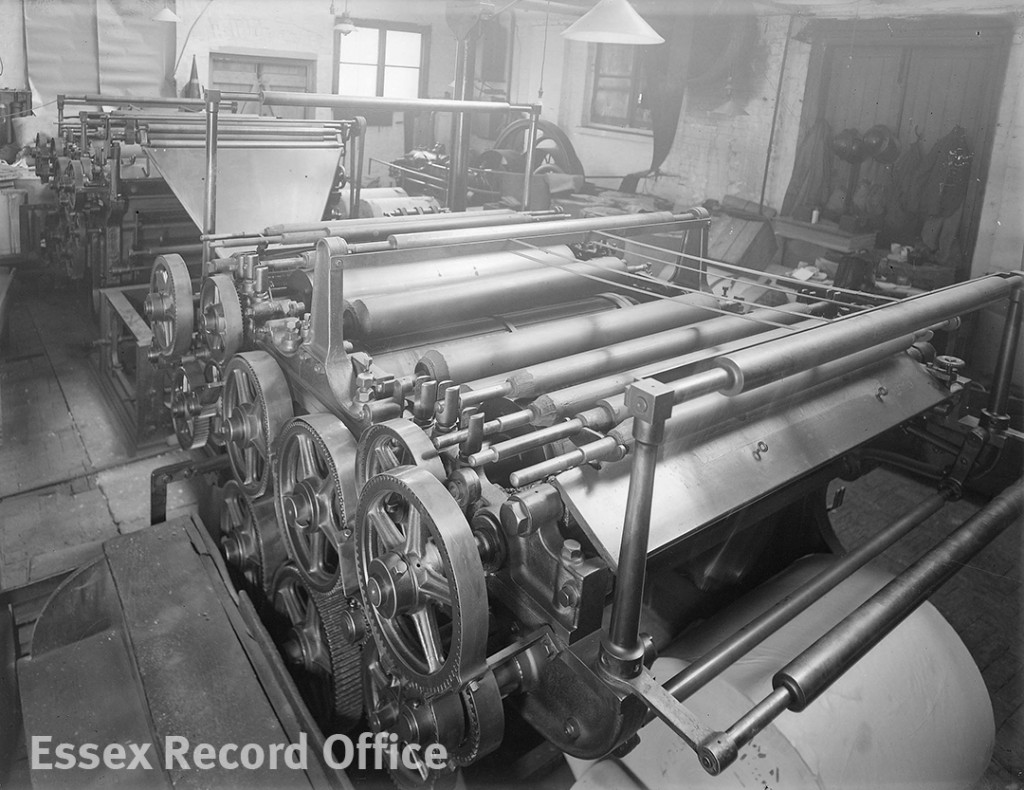
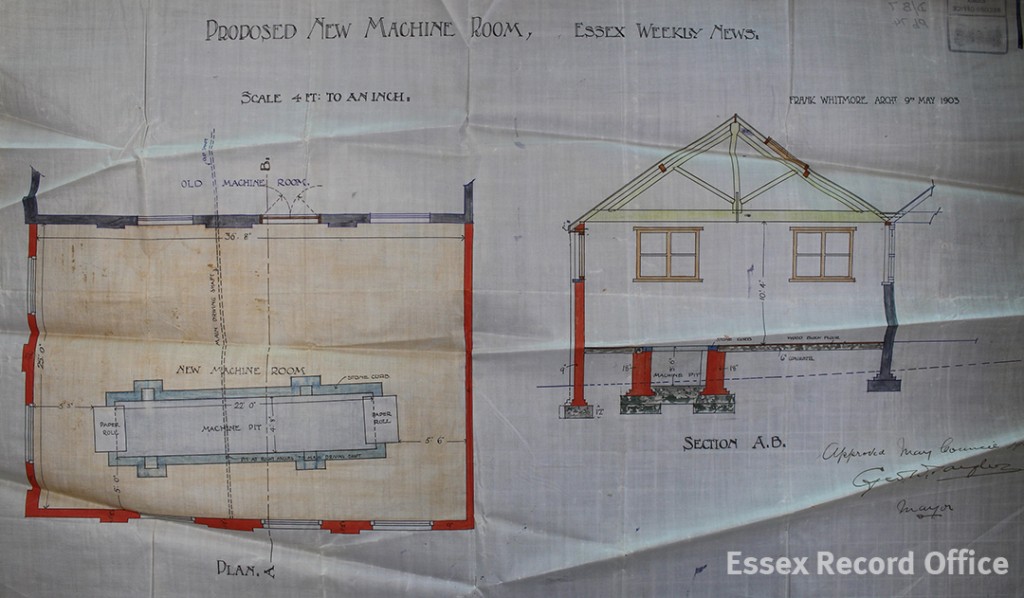
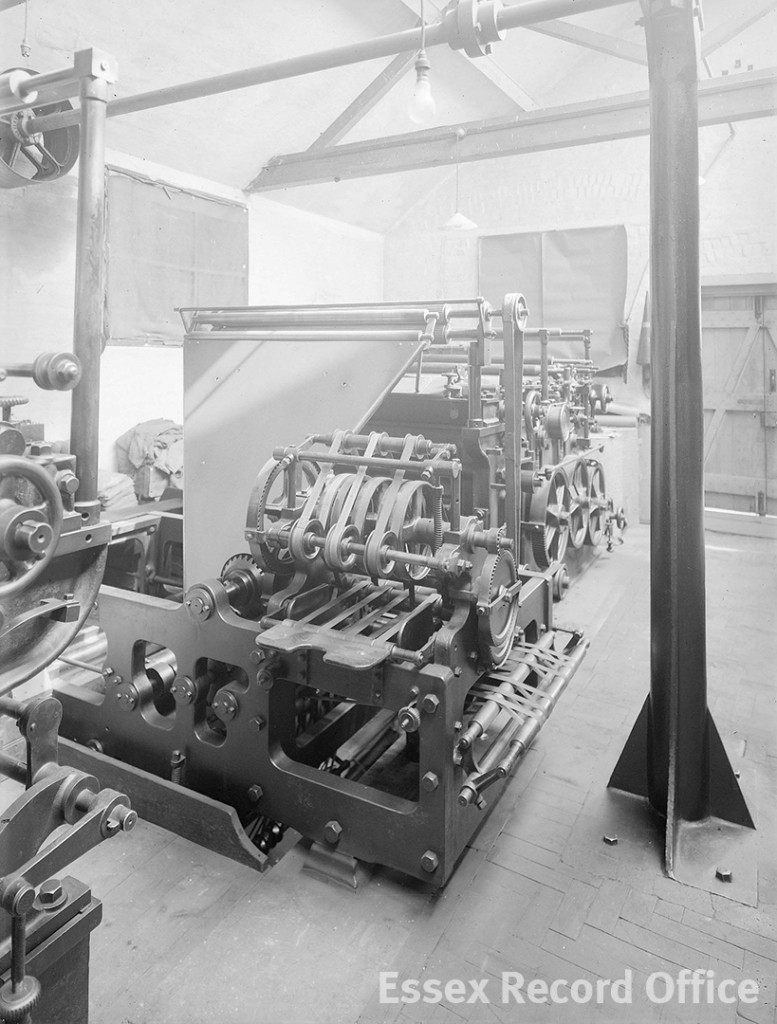
In 1869 the property was bought by John Taylor and Edward Robbins, who ran the Essex Weekly News. Various alterations were made to the interiors of the building, including the addition of a machine room in 1903. Images captured by Chelmsford’s preeminent photographer Fred Spalding, who lived just a few doors away, show us what the printing room looked like at this time.
The Essex Record Office fortunately possess several Spalding photographs which capture the machine room in action.
The Grade II listed building retains much of the original 18th century detailing today, despite having functioned in various capacities since it was built. The site is currently occupied by the Royal Bank of Scotland.
If you would like to find out more about this property see Hilda Grieve’s detailed history of Chelmsford, available in the ERO Searchroom. Alternatively, search document reference D/DU 755/45 on Seax for a large bundle of deeds relating to 26 High Street.