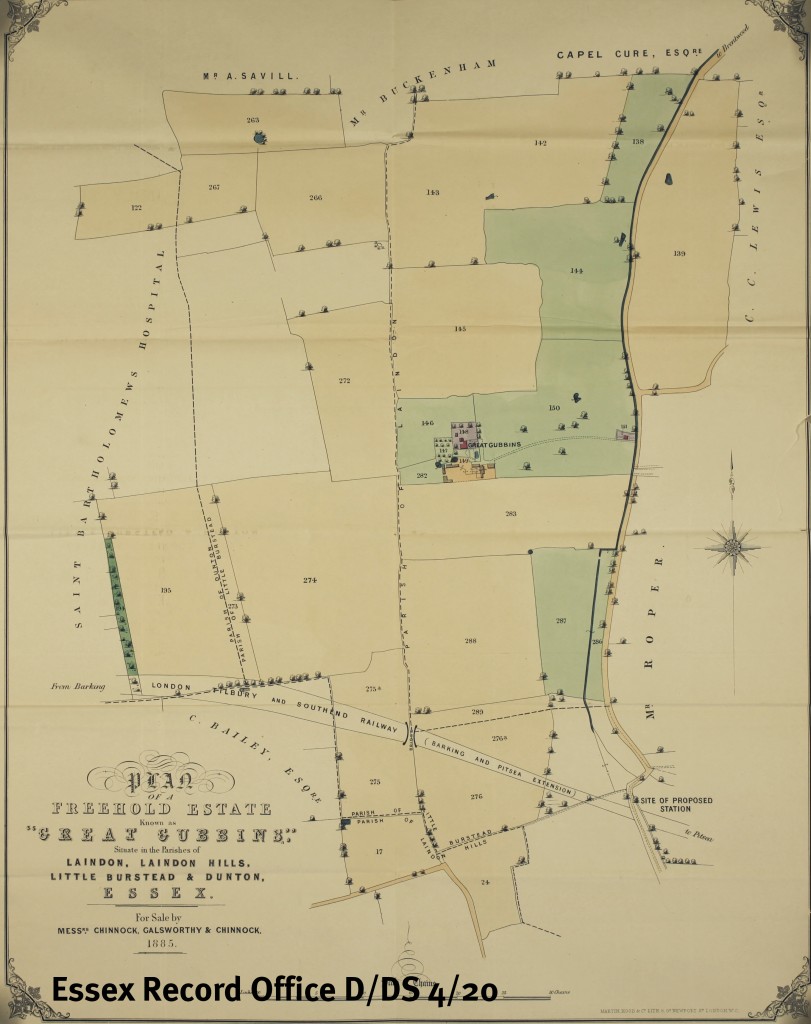
In this third post in our series looking at the history of Chelmsford High Street, Ashleigh Hudson looks at nos. 4-5 High Street through the centuries. Find out more about the project here.
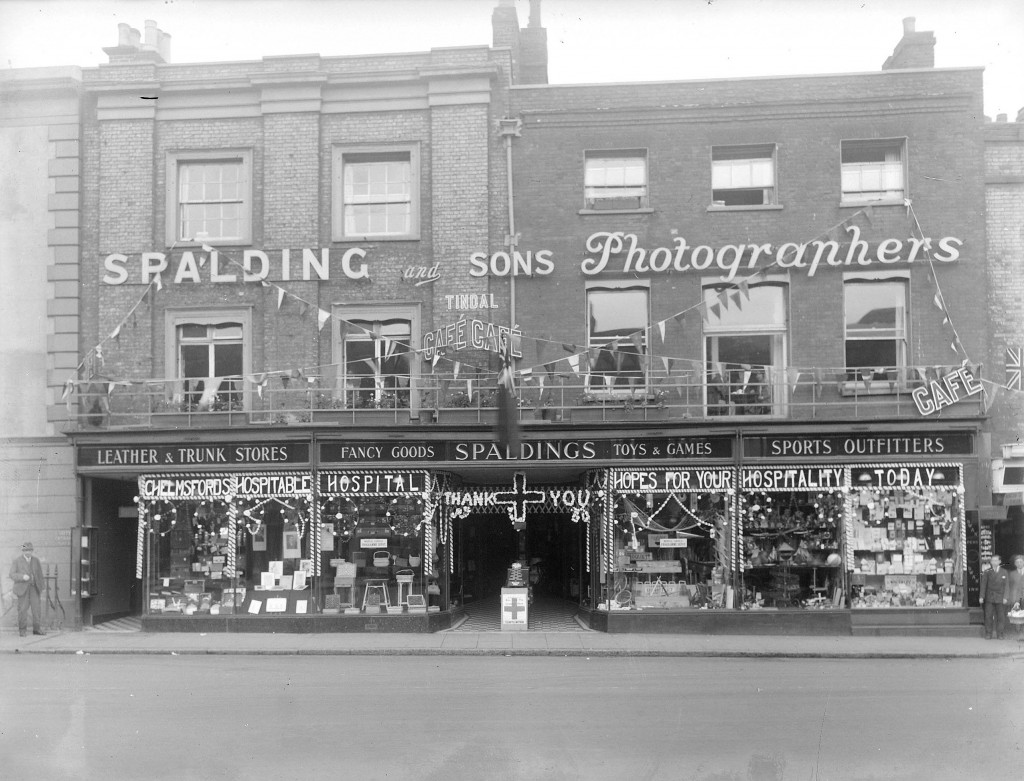
The current site of NatWest Bank at the north end of Chelmsford High Street is most commonly associated with the Spalding family who occupied the property from 1892. Fred Spalding junior ran a successful photography and fancy goods business which remained on the site until the mid-20th century. The property was built in the 18th century on the former site of the Crane Inn and was mostly used as a private residence until the arrival of the Spalding family.
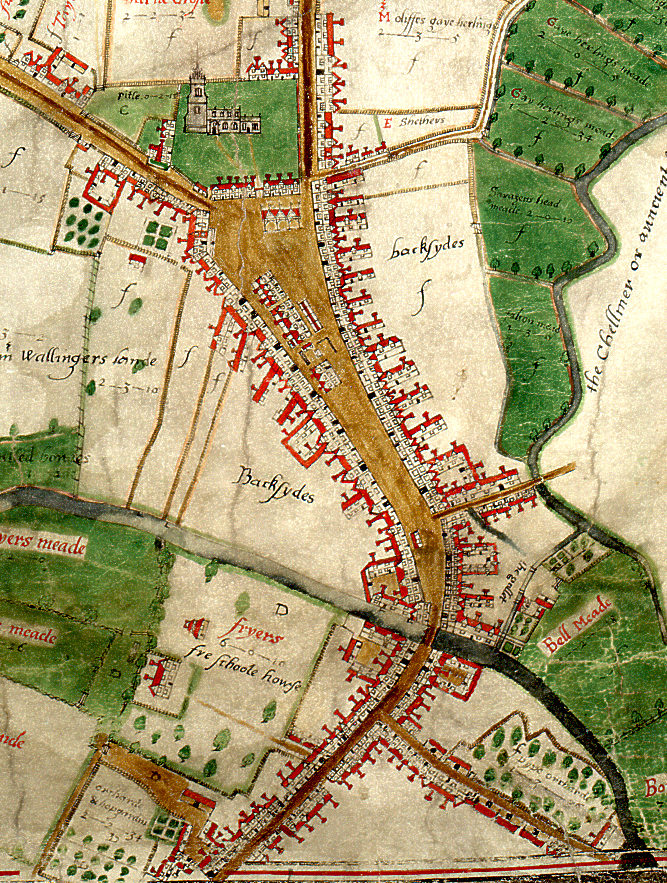
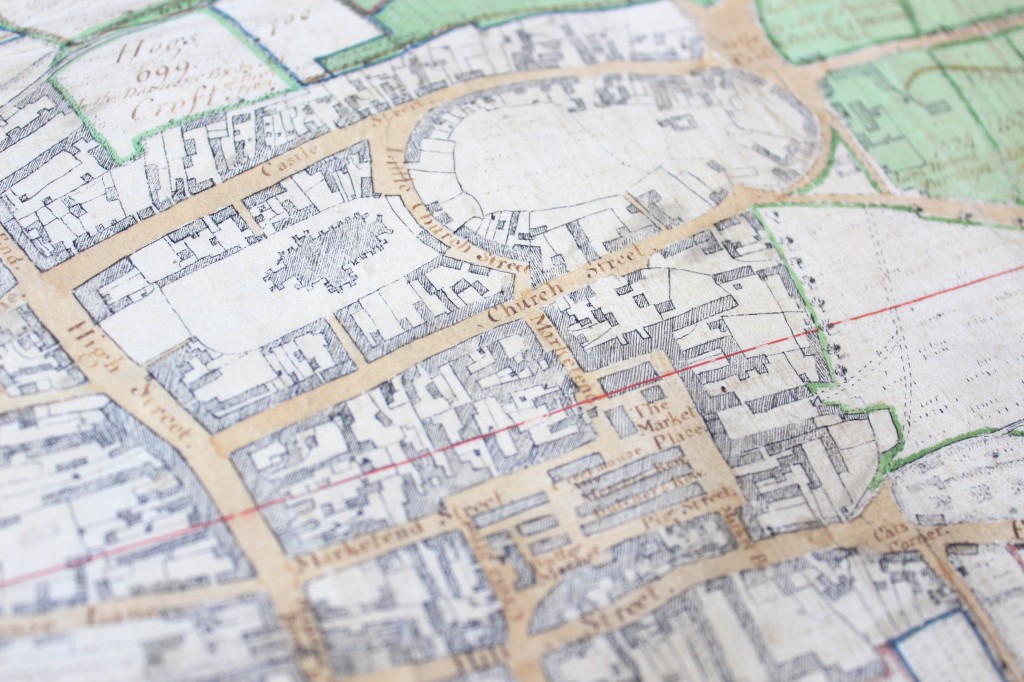
During the 16th century the Crane Inn, which was owned by Sir Thomas Mildmay, occupied the sites of 4-6 high street. The Crane Inn and yard, which is visible on the Walker Map, comprised numerous buildings which were progressively divided into smaller, individual properties during the 18th century. Number four was purchased by Thomas Old, a wine and brandy merchant, who rebuilt the property in 1784. The owner of number 5, Robert Tweed, perhaps inspired by his neighbour, rebuilt his own property the following year. The properties continued to function as private residences through to the 19th century.
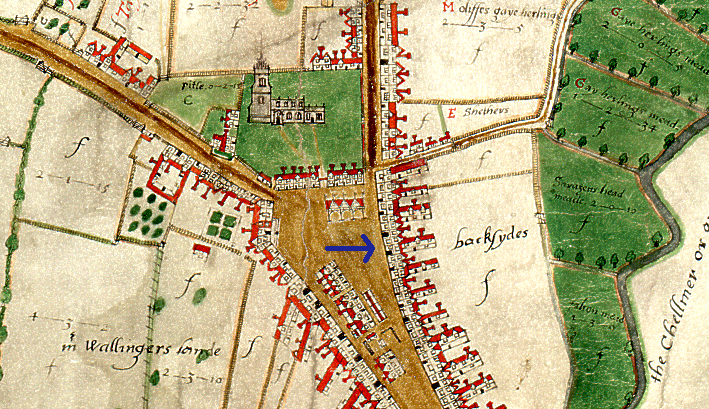
Extract from John Walker’s 1591 map of Chelmsford, showing the north end of the High Street where the Crane Inn was situated. (D/DM P1)
From 1871 number 4 was owned and occupied by wine merchant John Champ. The Champ residence was an attractive three-storey brick property.
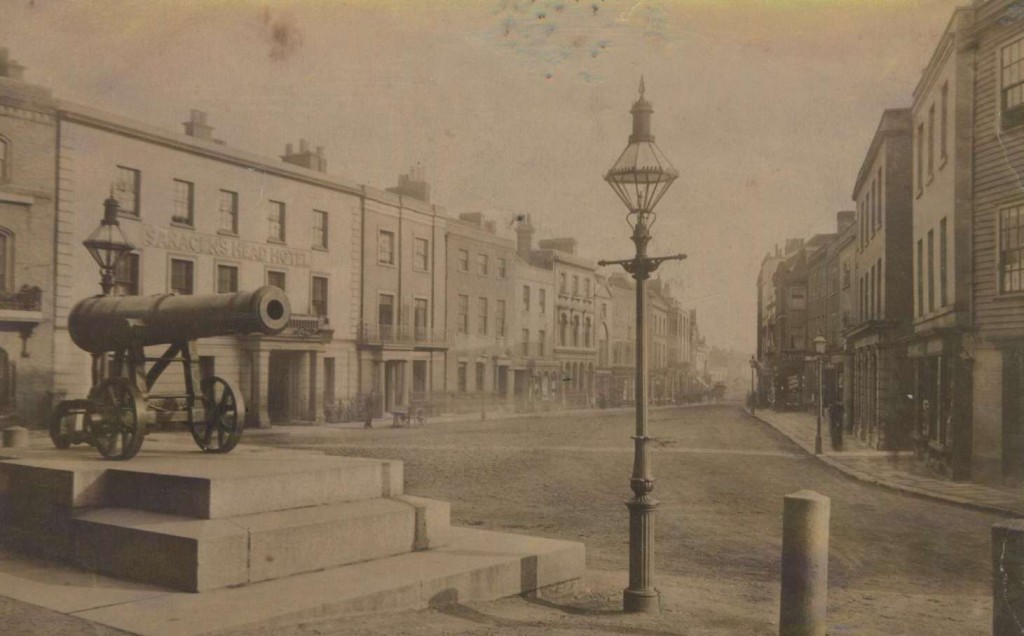

Early photo of the High Street taken from the Shire Hall. The Champ residence can be seen on the right of the Saracen’s Head Hotel.
Champ conducted a successful wine and brandy import business from the premises which was frequently advertised in the local newspapers. Ironically, Mr Champ himself did not drink. Chelmsford Mayor Frederick Spalding recalled the following encounter whereby a well-known local tradesman paid a visit to the residence to observe the different vintages of port and wine in Mr. Champ’s well-stocked cellar. Quoting Mr. Champ:
“That is a very special port, and I should say from the age and condition that it is worth quite 15/- a bottle.” On arriving back at the office he [Champ] said to his visitor, “Can I offer you anything to drink?” “Yes” came the quick reply, “I should like a glass of port from the special bin you showed me.” Mr Champ hesitated, but would not go back on his word. He brought a bottle and it is said the gentleman finished it before he left.”
The property obviously made an impression on the young Fred Spalding who purchased it shortly after John Champ’s demise in 1892. Fred Spalding’s father, also called Fred, was a self-taught photographer who got into the business really as the art itself was taking off. Fred senior moved to Chelmsford around the same time, where he set up business on Tindal Street. The Tindal Street store proved prosperous and this was where the young Fred Spalding learnt the family trade.
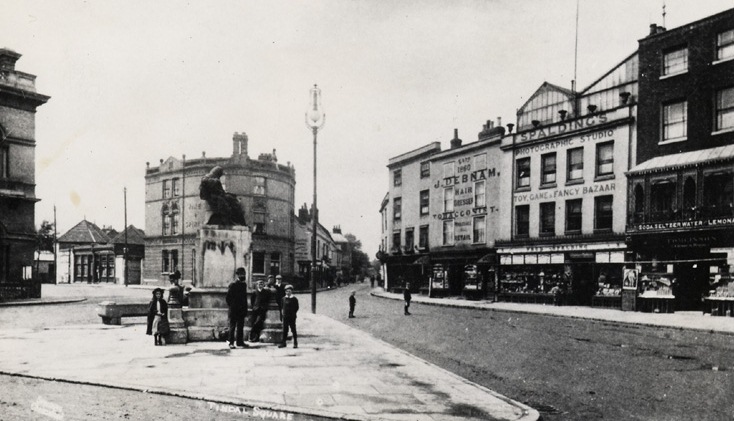

Photograph of Tindal Square in the late 1860s. In the centre of the image is the original Spalding shop. The premises is fairly small and quite understated in comparison to the later shop situated on 4-5 5 High Street. A glass studio, necessary for photographers prior to the introduction of artificial lighting, is visible on the roof of the property.
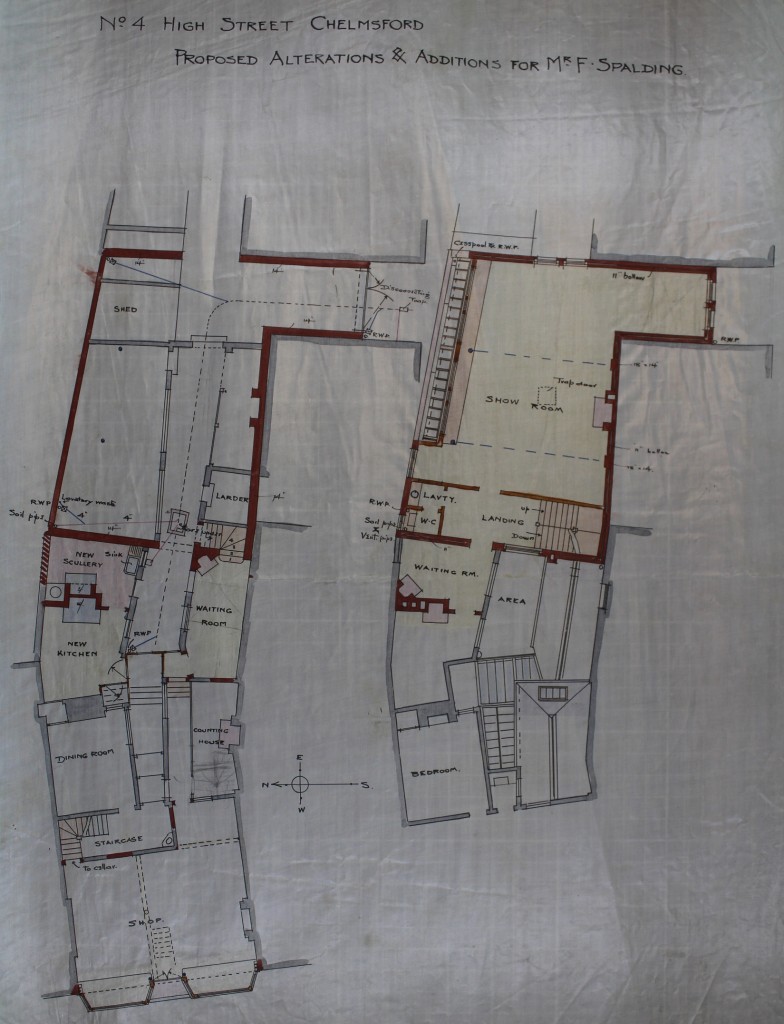
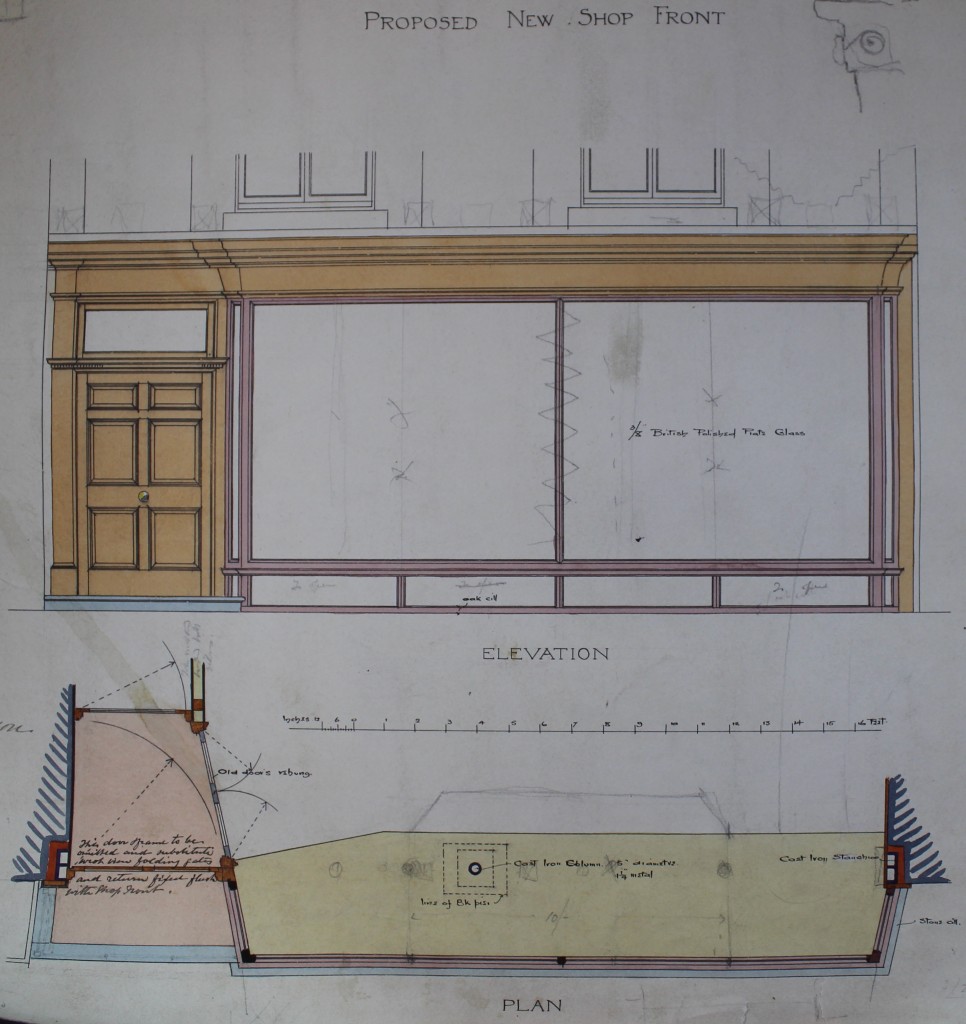
By 1892, Fred Spalding junior was on the hunt for new premises to accommodate his expanding business. John Champ’s residence, described by a sale advertisement as occupying the most ‘commanding and desirable’ location in town, came up for sale in October of that year. Spalding surely agreed with the advertisement having purchased the property shortly after. He promptly commissioned the noted local architect Frederic Chancellor to redevelop the existing buildings to enable to smooth transition from ‘house’ to ‘shop’. Chancellor’s plans for the changes have survived and are deposited among his practice’s papers at ERO.
The most noticeable change was the addition of large, glass display windows at street level which were used to display photographs and goods for sale.
Spalding’s skilfully arranged displays were renowned for captivating passers-by and drawing business into the shop. On one particular occasion in 1905, a Spalding’s display unintentionally exposed simmering tensions between the local constabulary and the town’s tradesmen. Crowds had gathered outside the shop window to view photographs taken of a recent railway accident in Witham. The Chief Constable of Essex later wrote a letter to the Town Council complaining that the display was obstructing the use of the pathway causing pedestrians to step into the road. The Constable scathingly wrote:
“Mr Spalding evidently thinks that the curtilage of his premises extends to the whole footpath and a part of the road…During my experience of over five years in this town I have found that the greater offenders against the laws of obstruction are the tradespeople…”
Mr Spalding, dismayed by the ‘trivial’ nature of the complaint responded:
“It is the ambition of tradesmen to make the best show they can of their goods. If the police are going to try to stop the tradesmen from showing their goods, the sooner I shut up shop the better.”
The issue was discussed at length by the Town Council where the complaint was universally agreed ridiculous, with Councillor Waller concluding:
“It was the people on the path who made the obstruction. If the police could not move them on they don’t seem to me to be competent.”
The shop continued to thrive throughout the first half of the twentieth century. The large crowd, depicted in the photograph below, have gathered outside the Spalding shop to await the arrival of Father Christmas, who made an annual detour to visit a grotto located inside the premises. This tradition was a popular and very well attended event.
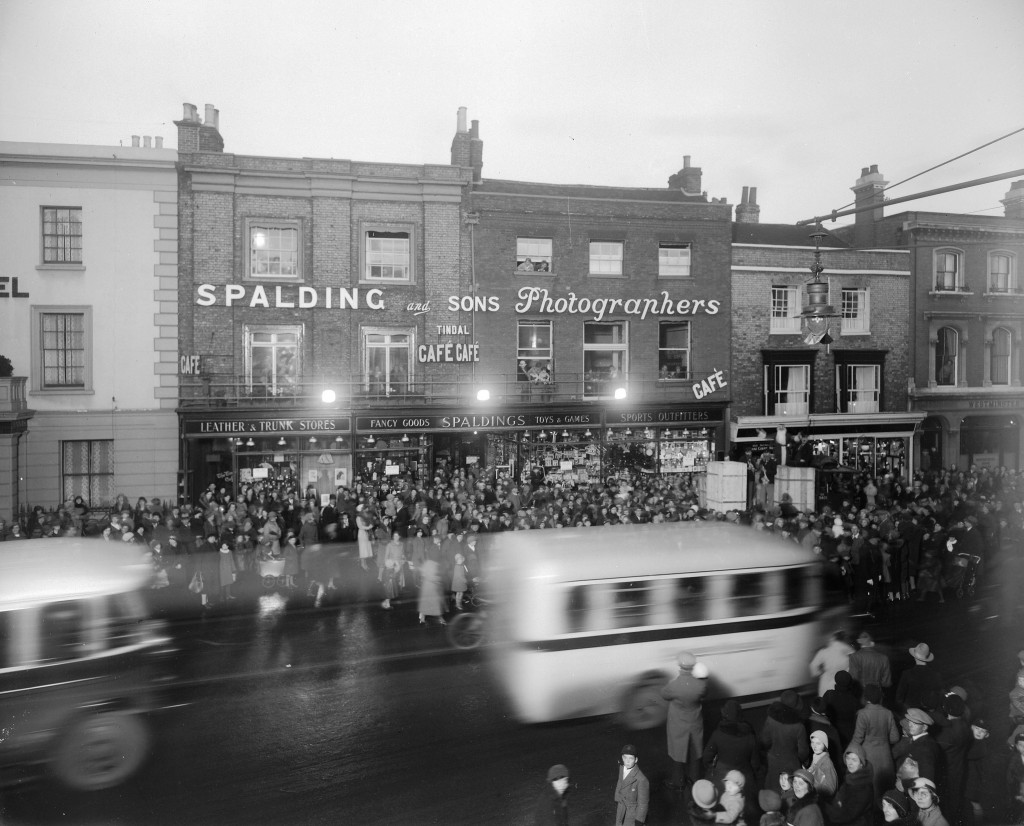

The annual visit from Father Christmas to the Spalding shop was an extremely popular and well-loved event. (SCN 3914)
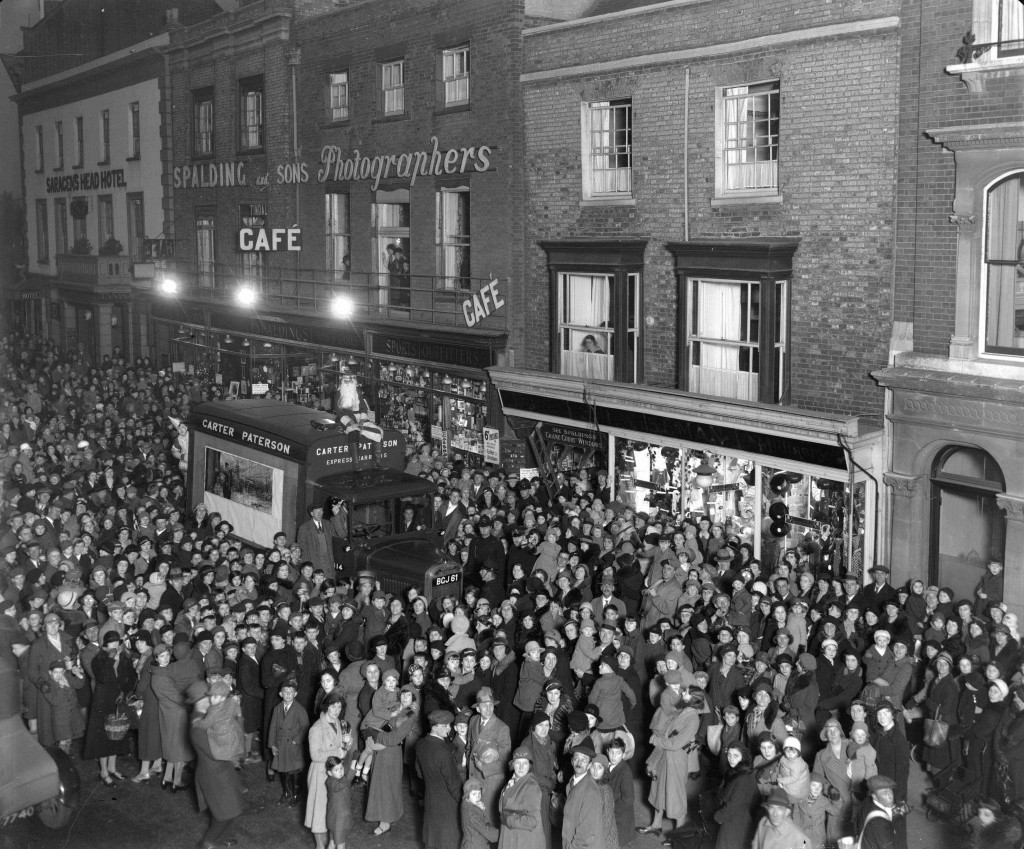

A large crowd eagerly awaiting the arrival of Father Christmas outside the Spalding shop in the 1920s. (SCN 3995)
The shop continued to operate during the war years, providing emergency shelter for up to 150 people. Shoppers caught on the high street during an air raid could find safety in the extensive basement below the Spalding shop.
Frederick Spalding survived the war but died shortly after. He was a much revered member of the town, having served for over 50 years on the Town Council as well as three consecutive terms as Mayor. The closure of the shop swiftly followed, marking the end of an era for Chelmsford photography. For the best part of a century, the Spalding family captured both the history and character of the town. The legacy of this endeavour can be found in the vast collection of photographs which are housed in the Essex Record Office. The Spalding image collection, which number in excess of 7000, is available for viewing from the Essex Record Office Searchroom.
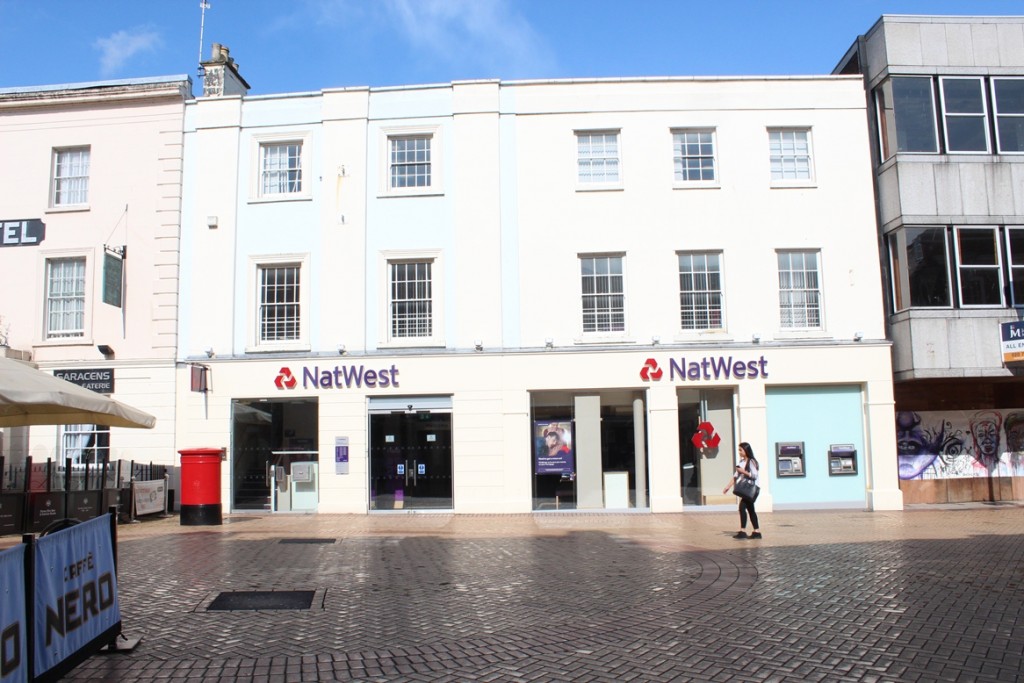
At first glance the current NatWest building appears radically different but in reality, the original features of the 18th century building still remain and are visible beneath the layers of pale blue and cream paint.
If you would like to find out more about Fred Spalding and his photography shop see The World of Fred Spalding by Stan Jarvis available in the ERO Searchroom. Alternatively pop into the ERO and browse the fantastic collection of Spalding images located in the Searchroom.