This month marks the 50th anniversary of the creation of the 5 London Boroughs of Barking & Dagenham, Havering, Redbridge, Newham and Waltham Forest in the metropolitan area of the ancient county of Essex.
To mark this anniversary, we have cheated slightly with Document of the Month and chosen images of those places when they were still part of Essex.
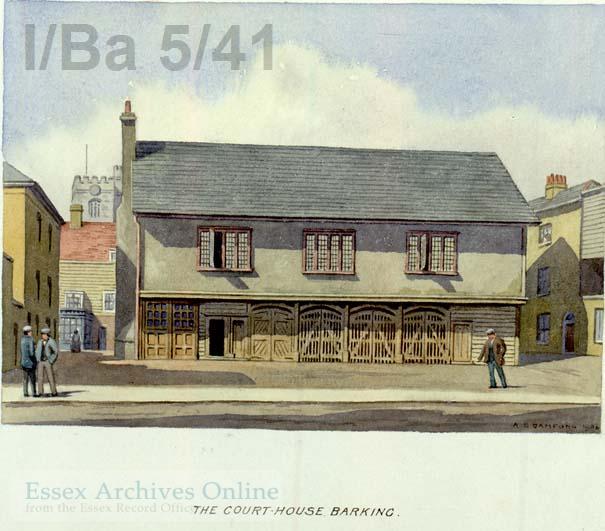
The old Court House or Market Hall or Old Town Hall at Barking was built and paid for by Elizabeth I. By 1920 it had fallen into disrepair and was demolished in 1923.
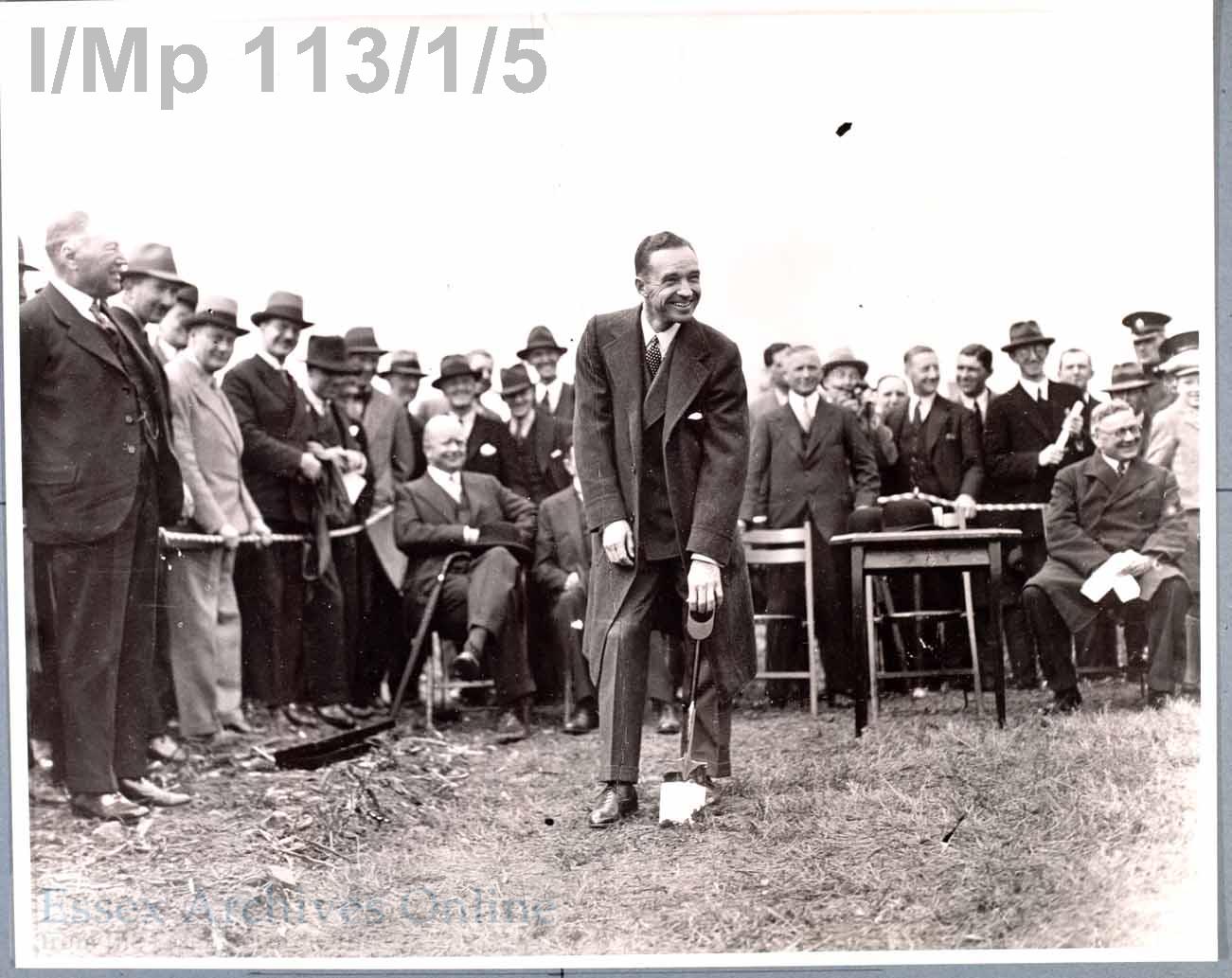
Dagenham will always be associated with Fords. This photograph shows Edsel Ford cutting the first sod for the factory c. 1929.
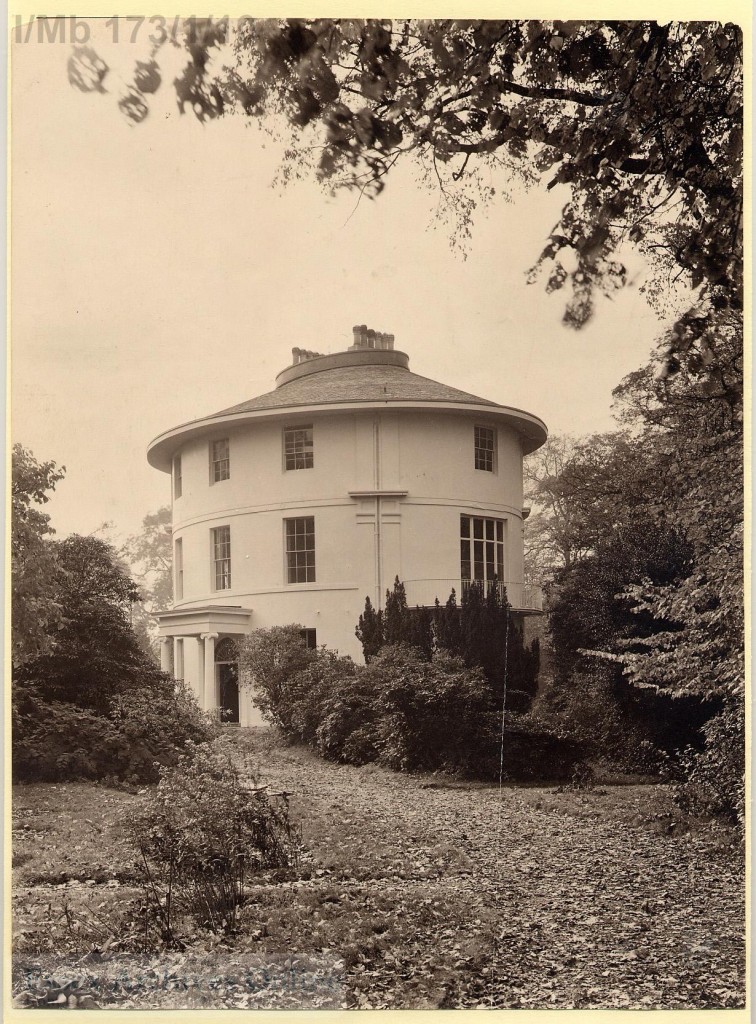
Havering was named for the ancient Royal Liberty of Havering-atte-Bower. The Round House, Havering was built in 1792 for William Sheldon, a wealthy tea merchant, and was later home to Rev Joseph Pemberton who developed the hybrid musk rose in the 1900s.
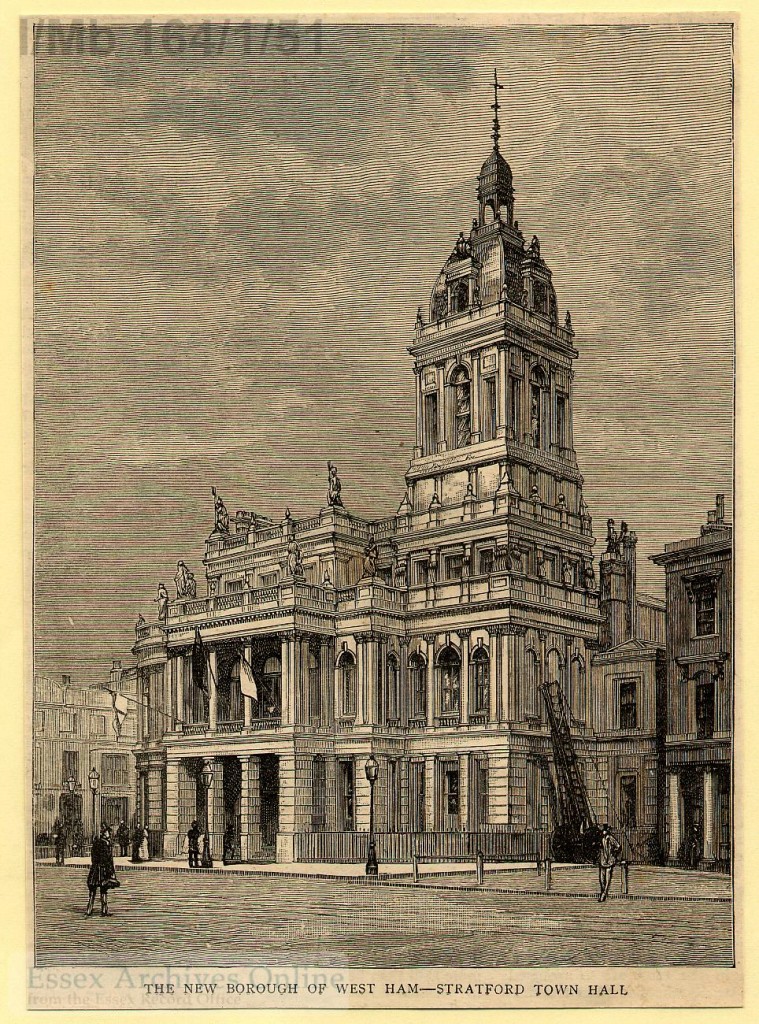
Newham was formed from the County Boroughs of West Ham and East Ham. This illustration shows the Old Town Hall at Stratford, built in 1869.
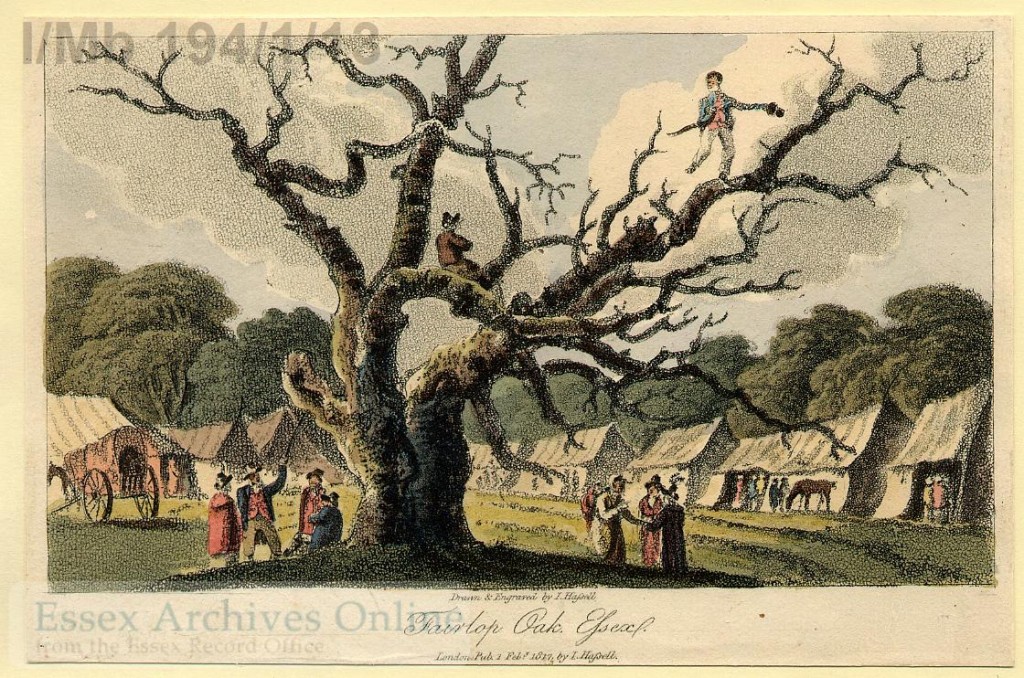
Redbridge was named for a bridge over the River Roding. Situated in the Borough was the Fairlop Oak, an ancient place for fairs. Its name continues in the Fairlop Waters Country Park.
Vestry House, Walthamstow is where the Waltham Forest archives are held. This watercolour is by A. B. Bamford and dates from 1926.