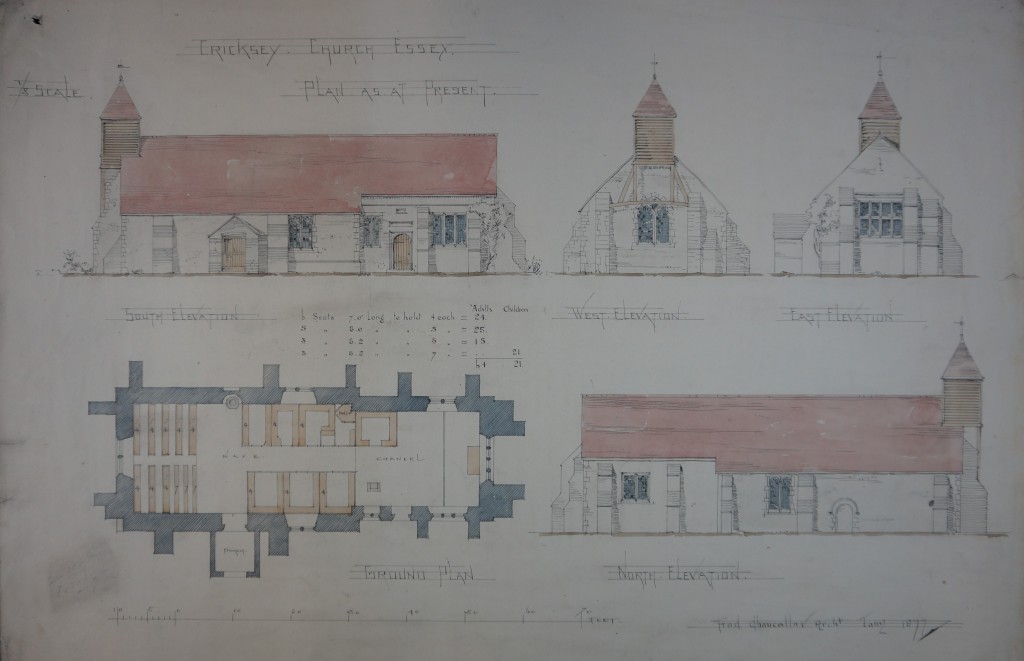
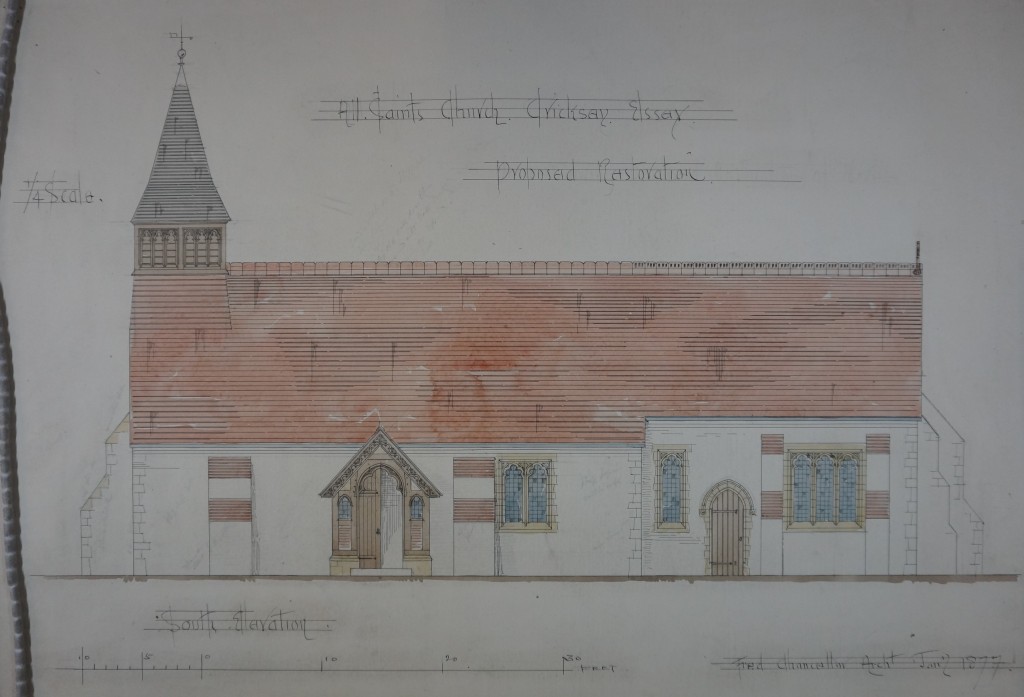
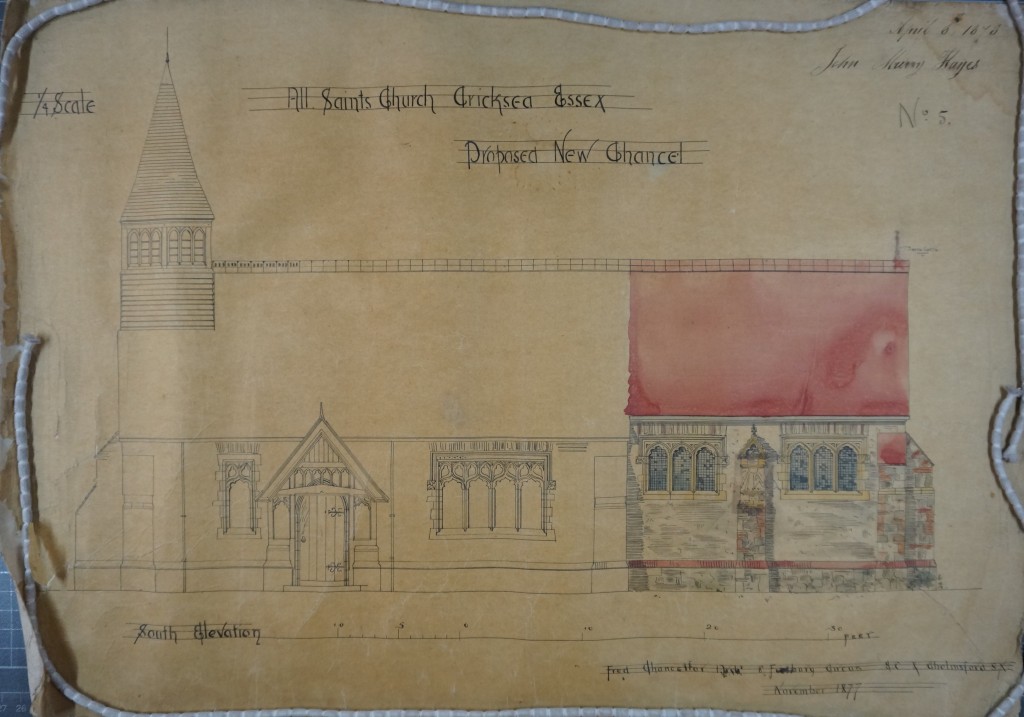
We have previously written about Essex girl Kate Luard, who served as a nurse on the Western Front throughout the whole of the First World War. One of Kate’s relatives, Caroline Stevens, is writing a blog about Kate’s wartime experiences, and here, 100 years after they were written, shares with us some of Kate’s diary entries for spring 1915.
On August 6, 1914, two days after the British Government declared war on Germany, Kate enlisted in the QAIMNSR (Queen Alexandra’s Imperial Nursing Service Reserve). During her first year in France and Belgium she serves on the ambulance trains until, on April 2, 1915, she receives movement orders to report to the Officer Commanding at No.4 Field Ambulance. This brought her close to the front line and she referred to this in her diary as ‘life at the back of the front’. Here she also worked in an Advanced Dressing Station.
A Field Ambulance was a mobile front line medical unit for treating the wounded before they were moved to a casualty clearing station. Each division would have 3 field ambulances which were made up of 10 officers and 244 men. A field ambulance would include stretcher bearers, nursing orderlies, tented wards, operating theatre, cookhouse, wash rooms and a horsed or motor ambulance.
The field ambulances set up and supplied Advanced Dressing Stations which were basic care points providing only limited medical treatment and had no holding capacity. The wounded were brought here from Regimental Aid Posts which were only a few metres behind the front line in small spaces such as a support or reserve trench.

An advanced dressing station of the Royal Army Medical Corps (RAMC) on the Montauban – Guillemont Road. September 1916 (Imperial War Museum)
From Kate’s diary:
April 2nd, 1915. Good Friday
So hell became heaven and here I am at railhead waiting for a motor ambulance to take me and my baggage there.
11 A.M. Had an interesting drive here through a village packed with men billeted in barns and empty houses–the usual aeroplane buzzing overhead, and a large motor ambulance convoy by the wayside. We are in the town itself, and the building is labelled No.4 Field Ambulance Dressing Station for Officers.
Still Good Friday, 10pm. (Kate spends a luxurious night in Maire’s Château where Generals and officers are usually billeted.)
April 3rd, 1915. Easter Eve, 10 P.M.
Have been on duty all day. They [the wounded] are nearly all evacuated in a few days, so you are always getting a fresh lot in.
I found my own new billet this morning before going on duty; it is a very old little house over a shop in a street off the big Place. It is a sort of attic, and I am not dead sure whether it is clean on top and lively underneath, but time will show.
April 7th, 1915. In bed, 10.30 P.M.
We are busy all day admitting and evacuating officers. A very nice Brigade-Major came in, in the night, with a shell wound in the shoulder. This morning a great jagged piece was dug out, with only a local anaesthetic, he stuck it like a brick, humming a tune when it became unbearable and gripping on to my hand.
I was off at 5pm and went to Beuvry, the village two and a half miles away that was shelled last week; it is about half-way to the trenches from here. Met and passed an unending stream of khaki, the men marching back from their four days in the trenches, and all steadily trudging on with the same coating of mud from head to foot, packs and rifles carried anyhow, and the Trench Look which can never be described, and which is grim to the last degree. Each lot had a tail of limping stragglers. They said they’d had a very “rough” night last night – pouring rain – water up to their knees, and standing to all night expecting an attack which didn’t come off; but some mines had been exploded meant for their trench but luckily they only got smothered instead of blown to bits.
April 10th, 1915. 10.30pm.
It is difficult to settle down to sleep to-night: the sky is lit up with flashes and star shells, and every now and then a big bang shakes the house, above the almost continuous thud, thudding, and barking of the machine-guns and the crackling of rifle firing; they are bringing in more to-day, both here and at the hospice.

Stretcher cases awaiting transport to a Casualty Clearing Station lie on the ground outside a dressing station at Blangy near Arras, April 1917 (Imperial War Museum)
April 16th, 1915
This afternoon I saw a soldier’s funeral, which I have never seen before. He was shot in the head yesterday, and makes the four hundred and eleventh British soldier buried in this cemetery. The French gravedigger told me there was another to be buried this afternoon. It was very impressive and moving, the Union Jack on the coffin (a thin wooden box) on the waggon, and a firing party, and about a hundred men and three officers and the Padre. It was a clear blue sky and sunny afternoon. The graves are dug trenchwise, very close together, practically all in one continuous grave, each with a marked cross.
April 26th, 1915. 11 P.M.
We have been admitting, cutting the clothes off, dressing and evacuating a good many to-day. There is a great noise going on to-night, snapping and popping, and crackling of rifle firing and machine guns, with the roar of our 9.2’s every few minutes.
 The above are extracts from Kate’s first book ‘Diary of a Nursing Sister on the Western Front 1914-1915’. Go to www.kateluard.co.uk and click on ‘blog’ for entries which are posted on the same day as the events of 100 years. You can also read all the extracts which you have missed.
The above are extracts from Kate’s first book ‘Diary of a Nursing Sister on the Western Front 1914-1915’. Go to www.kateluard.co.uk and click on ‘blog’ for entries which are posted on the same day as the events of 100 years. You can also read all the extracts which you have missed.
During her time in France, Kate exchanged numerous letters with her family at home in Birch near Colchester. The majority of these letters are held in the Luard archives at the Essex Record Office, Chelmsford.