For the last few months ERO has hosted two student placements jointly funded by the Friends of Historic Essex and University of Essex. They have both written for us about their experiences and what they have discovered here at ERO. In his blog post below Aaron Archer explores the huge wealth of information held within parish Poor Law documents. If you enjoy this article, Aaron has also written a separate article for the Friends of Historic Essex – News – Friends of Historic Essex

During my placement at the Essex Record Office, I have been cataloguing the parish records of north-east Essex. Dating broadly from the late seventeenth century through until the mid-nineteenth century, many of the documents contained within this collection relate to the Poor Law and the daily administration of the various parishes.
The ‘old Poor Law’ which concerns these documents began with the acts of Elizabeth I between 1598 and 1601, and effectively outlined those who were considered ‘the deserving poor’ and those that ‘refused to work’.[1] The responsibility of this poor relief system lay with the parishes, particularly the churchwardens and overseers of the poor, who enacted the day-to-day workings of the system.[2]
Whilst my time has largely involved cataloguing these various documents, such as settlement certificates, apprenticeship indentures and removal orders… I must confess – I have been unable to resist taking some notes on some of the more colourful or exceptional stories uncovered within these records!
Also, I should preface this by stating that all of what I record here has been uncovered with minimal research – and that alone should demonstrate the wealth of information and the variety of stories that one could find if you are actively seeking to research a similar topic (or looking for a research starter!).
Let us begin the examples of William Allen and Deborah Brooks. These names occur more than once each within the bastardy bonds of the parish of St Peter’s in Colchester.
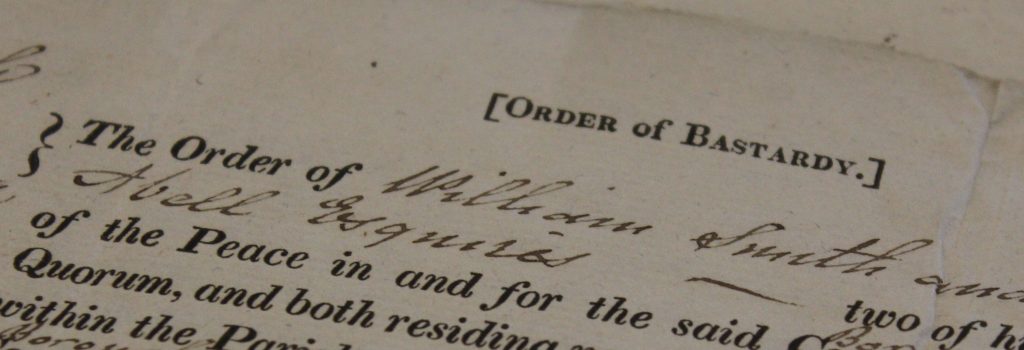
On 10 June 1823, Deborah Brooks underwent a voluntary examination (D/P 178/15/2/4) relating to the illegitimate child she had recently given birth to. Such an examination was necessary to determine whether the child would be chargeable to the parish in which the examination was taking place. During this, Brooks reputed that William Allen, a blacksmith from Brightlingsea, was the father of the child. As such, Allen would be liable to pay a bastardy bond of £2 immediately to the churchwardens of St Peters for any costs incurred by parish, then a further two shillings per week in support of the child, and a further sixpence per week to support Brooks. Clearly, illegitimate births like these were costly. According to the National Archives’ currency converter, £2 was the equivalent of 13 days wages of a skilled worker.
Yet, this is not the last we hear of William Allen. On 2 December 1823, Alice Cook of St Peter’s, Colchester undertook a voluntary examination relating to her illegitimate pregnancy (D/P 178/15/2/5). Once again, the name William Allen was stated when it was questioned who the father may be. This time, William Allen was said to be a drover from Ardleigh. In this instance, Allen was ordered to pay a bastardy bond of £1, 16 shillings to St Peter’s, then a further two shillings and sixpence per week to Alice Cook and the child once it was born.

Of course, this very well could have been a separate individual, however it is also a stretch that two women from the same parish became pregnant to two different men sharing the same name, and only six months apart… If these cases do indeed involve the same individual, then William Allen certainly was an unfortunate soul to fall into the same situation twice – and with only 6 months in between cases!
But we must not forget Deborah Brooks either. Her name also appears again on the 10 September 1824. Again, she underwent an examination regarding her illegitimate pregnancy, and on this occasion, Charles Wenlock, a mariner from Brightlingsea, was the reputed father (D/P 178/15/2/8). The parish of St Peter’s wrote up a bastardy bond for £4 and one shilling, plus the further weekly one shilling and sixpence for the child, and sixpence per week for Brooks, however it appears that things were not so simple for Wenlock. An attached note states that Wenlock had changed addresses during this period and thus was unaware of the money he now owed. When he was eventually found on 29 June 1827, he owed a total of 146 weeks of unpaid maintenance amounting to £10 and 19 shillings! For reference, this was about two months wages for a skilled tradesman.

These stories present some interesting implications. Firstly, and most apparently, these instances offer an insight into relationships and people’s perceptions towards sex. Clearly people were frequently engaged in physical relationships outside of wedlock despite religious doctrine and expectations still being a considerable part of society. Moreover, these relationships were not just between people from neighbouring parishes, but sometimes parishes miles apart – suggesting how mobile people were on a regular basis.
Secondly, there is the suggestion that bastard births were a broader social problem for early modern parishes, and one that exacerbated an already stretched and flawed relief system. A small note amongst St Peter’s records states that in 1819 a total of £1368, 11 shillings and 4 pence was levied in local rates. Of this, £1247, 7 shillings and 1 pence was expended in poor relief alone, highlighting that there was little flexibility for further strain on the existing system. This made it imperative for parishes to ensure illegitimate births were chargeable to the correct parishes to avoid footing the bill.
Unfortunately, this did lead to more tragic examples, too. For instance, the case of Ann Bugg, whose issues with the poor relief system and an illegitimate birth proved harrowing.
On 20 April 1816, Ann Bugg, a single woman living in St Peters, was removed from the parish with her child George (D/P 178/13/2/21), and was returned to her last legal settlement, St Mary in Whitechapel. This was not unusual, as parishes were likely to remove single men and women, probably to avoid instances of illegitimate births. Yet two months later, on 10 June 1816, the churchwardens of St Mary sent a copy of Ann Bugg’s bastardy examination to St Peter’s. In it, the churchwardens of St Mary suggest that the child was chargeable to St Peter’s rather than them, as the child was born there. The emergent argument here being one of an individual removed to their legal settlement, yet her child being born in another parish, with two overseeing parties unwilling to deal with the situation by placing the responsibility on each other.

As we have already seen, however, St Peters was particularly stringent in its budgeting and chose to argue the case rather than foot the bill. The situation escalated, and the Justices of the Peace were employed to address the situation. They officially recognised the complaint of St Peters on 8 July 1816 (D/P 178/15/5/1), and two days later issued an official summons (D/P 178/15/5/2) to the churchwardens of St Mary, on the grounds of their refusal to reimburse St Peters for the costs incurred for Ann Bugg’s bastard child. The matter was to be addressed at the next Quarter Sessions.
This was not to be the last of the story, however. In 1820, the issue arose again when the parish of St Mary once again wrote to St Peters (D/P 178/15/5/3), stating they had no knowledge of Ann Bugg’s child and the birth, and therefore refused any steps towards reimbursing St Peters for all the of the costs incurred. Meanwhile, during this four-year quarrel between the two parishes, it is unknown whether Ann Bugg received any support for herself or her child from either parish.
The last mention of this case comes from a small note dated 28 June 1821 (D/P 178/15/5/4). In it, an individual named John Bugg, agreed to reimburse St Peters for the costs incurred during the entire ordeal. This amounted to £4, 14 shillings, though the note states that at this point Ann Bugg’s child had passed away since.

Quite clearly, this unfortunate story highlights the problems associated with the patchwork-quilt like system of parishes and poor relief seen during the Poor Law. It both demonstrates the loss of a young life due to the financial worries and bickering of inter-parish relations, along with the neglect of individuals based on the grounds of “not our problem”. Thus, it is no surprise that the system was unsustainable and saw ‘reform’ in the 1830s – though, this had its own whole series of problems!
It should be clear by now that these parish records can contain some fascinating insights into the lives of early modern individuals. As a historian, I previously would not have considered the depth seen these documents, nor the kinds of stories I have uncovered with relatively little research. After all, these stories I have covered here have literally only come together whilst passing through the various stacks of documents that have slid across my desk.
With this piece I hope I have been able to shine a light on the stories that one can find within parish records, such as bastardy bonds and removal orders, and demonstrated the potential that they have. With them family historians can uncover a much deeper understanding of the movements of their ancestors and the struggles they faced. Meanwhile, there is plenty of room for historians to explore microhistories of individual lives of people like Deborah Brooks, William Allen, and Ann Bugg.
These parish records are fascinating, and I would strongly encourage people to expand their scope beyond the singular documents they seek. Rather than focus solely on a specific document, explore other documents within the same box number – you will be surprised at some of the stories you can uncover!
References
[1] Samantha Williams, Poverty, Gender and Life-Cycle Under the English Poor Law 1760-1834, (Croydon: Boydell Pres, 2011), p.2.
[2] W.E. Tate, The Parish Chest: A Study of the Records of Parochial Administration in England, Third Ed. (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1969), p. 30.










